Everyone on an installation has shared responsibility for security. This fundamental principle underscores the collective effort required to safeguard critical assets, information, and personnel. Embracing this shared accountability fosters a culture of vigilance, where every individual contributes to the overall security posture.
From the highest levels of leadership to the frontline personnel, each role plays a vital part in maintaining security. This article delves into the concept of shared responsibility, outlining the roles and responsibilities of individuals, the importance of training and education, and strategies for effective collaboration and risk management.
1. Defining Shared Responsibility
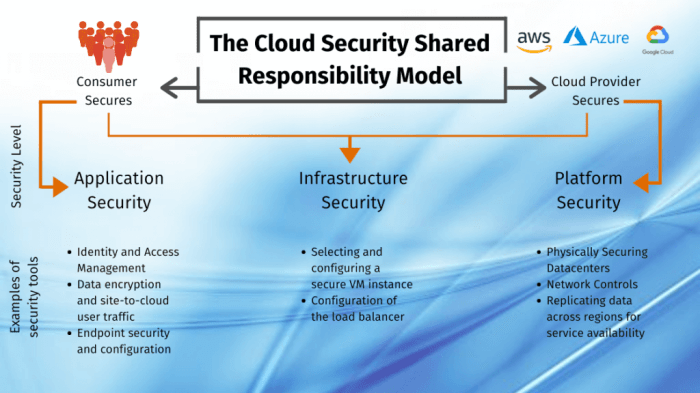
Shared responsibility for security refers to the concept that everyone within an organization has a role to play in maintaining the security of their information and systems. This includes both technical and non-technical personnel, as well as individuals at all levels of the organization.
Individuals can contribute to security by adhering to security policies and procedures, reporting security incidents, and being aware of potential security risks. By fostering a culture of security awareness, organizations can create an environment where everyone understands their responsibilities and takes an active role in protecting the organization’s information and systems.
2. Roles and Responsibilities: Everyone On An Installation Has Shared Responsibility For Security.

The specific roles and responsibilities of individuals in maintaining security vary depending on their position and level within the organization. However, some common roles and responsibilities include:
- Senior management is responsible for setting the overall security strategy and ensuring that adequate resources are allocated to security initiatives.
- IT personnel are responsible for implementing and maintaining security technologies, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
- End users are responsible for following security policies and procedures, and reporting any security incidents they encounter.
Failing to meet security obligations can have serious consequences for both individuals and the organization as a whole. Individuals may face disciplinary action, while the organization may face financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liability.
3. Training and Education

Ongoing training and education are essential for ensuring that individuals have the knowledge and skills necessary to fulfill their security responsibilities. Training programs should cover a variety of topics, including:
- Security policies and procedures
- Security risks and threats
- Incident response procedures
- Best practices for secure computing
Leadership plays a critical role in promoting security awareness by setting a positive example and communicating the importance of security to all employees. By investing in training and education, organizations can create a more secure environment and reduce the risk of security incidents.
4. Collaboration and Communication
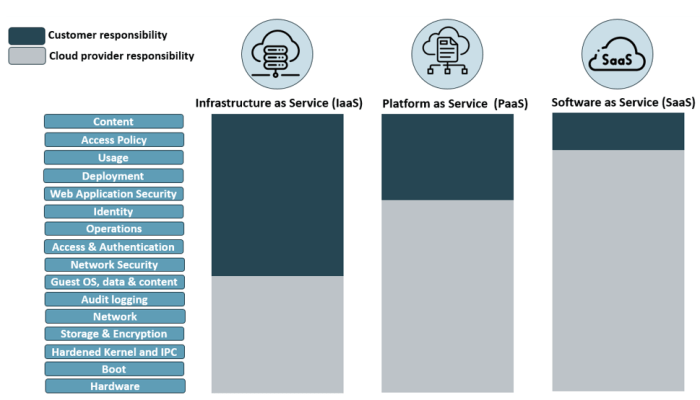
Collaboration and communication among individuals is essential for maintaining effective security. Individuals should be encouraged to share information about security risks and incidents, and to work together to develop and implement security solutions. Best practices for sharing information include:
- Establishing a central repository for security information
- Using email or instant messaging to share security alerts
- Holding regular security meetings
Technology can also facilitate collaboration by providing tools for sharing information and managing security incidents.
FAQ Explained
Who is responsible for security on an installation?
Everyone on an installation, regardless of their role or position, has a shared responsibility for security.
What are the consequences of failing to meet security obligations?
Failure to meet security obligations can have serious consequences, including data breaches, financial losses, and damage to reputation.
What is the role of training and education in security?
Ongoing training and education are essential for equipping individuals with the knowledge and skills they need to effectively contribute to security.