Select all the true statements about Trichinella species., a genus of parasitic roundworms that infect a wide range of animals, including humans. Trichinella infections, known as trichinosis, are a major public health concern due to their potential to cause severe muscle pain, fever, and gastrointestinal symptoms.
This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth overview of Trichinella species, their life cycle, transmission, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment, and public health significance. By understanding the intricacies of Trichinella infections, we can effectively prevent and control this debilitating disease.
Trichinella Species Overview
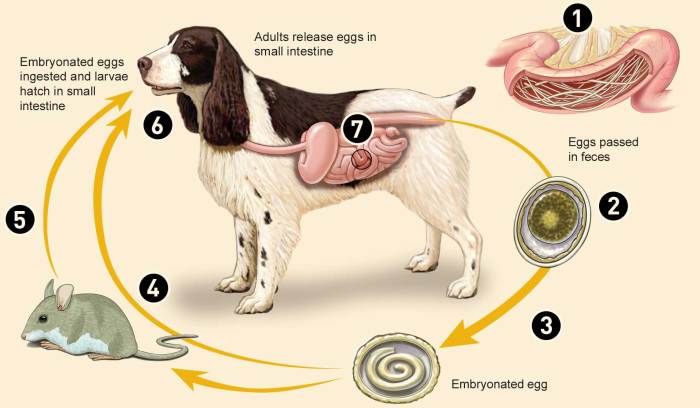
Trichinella species are parasitic nematodes that cause the disease trichinosis. They are small, roundworms that can infect a wide range of mammals, including humans. Trichinella species have a complex life cycle that involves two hosts, a definitive host and an intermediate host.
There are eight recognized species of Trichinella, but only four are known to infect humans: T. spiralis, T. nativa, T. britovi, and T. pseudospiralis. T. spiralisis the most common species found in humans and is responsible for the majority of cases of trichinosis.
Trichinella species are found worldwide, but they are most common in areas where there is a high consumption of raw or undercooked meat from infected animals.
Pathogenesis and Clinical Manifestations
Trichinella infections are caused by the ingestion of larvae in undercooked meat. The larvae are released from the meat in the stomach and then invade the intestinal mucosa. They then migrate through the bloodstream to skeletal muscle, where they encyst and develop into adult worms.
The clinical manifestations of trichinosis can vary depending on the number of larvae ingested. Mild infections may cause only mild muscle pain and fever. More severe infections can cause severe muscle pain, fever, gastrointestinal symptoms, and even death.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Trichinosis is diagnosed by serological tests or muscle biopsies. Serological tests detect antibodies against Trichinella antigens, while muscle biopsies can identify the larvae or cysts in muscle tissue.
Treatment for trichinosis involves antiparasitic drugs, such as albendazole or mebendazole. These drugs can kill the adult worms and prevent the larvae from developing into adult worms.
Public Health Significance: Select All The True Statements About Trichinella Species.

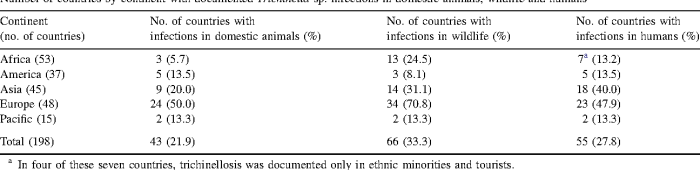
Trichinosis is a public health concern in many parts of the world. The disease can be prevented by cooking meat thoroughly and avoiding the consumption of raw or undercooked meat from infected animals.
Food safety measures are essential for preventing trichinosis. These measures include inspecting meat for Trichinella larvae, cooking meat to a safe internal temperature, and freezing meat for at least 20 days at -15°C (-5°F) or for at least 3 days at -20°C (-4°F).
Clarifying Questions
What is the primary mode of transmission for Trichinella infections?
Ingestion of raw or undercooked meat containing Trichinella larvae.
What are the most common clinical manifestations of trichinosis?
Muscle pain, fever, gastrointestinal symptoms, and facial edema.
How is trichinosis diagnosed?
Through serological tests and muscle biopsies.
What is the treatment for trichinosis?
Antiparasitic drugs and supportive care.
What are the key public health measures for preventing trichinosis?
Thorough cooking of meat, food safety practices, and public education.