Embark on an educational journey with our comprehensive prokaryotic cells worksheet answer key, a valuable resource that unravels the intricate world of prokaryotes. Delve into the fundamental characteristics, diverse structures, metabolic processes, and evolutionary history of these fascinating organisms.
This meticulously crafted answer key provides a clear understanding of prokaryotic cell biology, addressing common misconceptions and providing in-depth explanations of complex concepts. Explore the absence of membrane-bound organelles, the significance of ribosomes, and the remarkable adaptations that enable prokaryotes to thrive in diverse environments.
1. Prokaryotic Cell Overview
Prokaryotic cells are the simplest and most ancient type of cells. They are characterized by their small size, lack of membrane-bound organelles, and a single, circular chromosome. Prokaryotic cells are found in a wide variety of habitats, including soil, water, and the human body.
One of the most distinctive features of prokaryotic cells is their lack of membrane-bound organelles. This means that all of the cell’s functions are carried out in the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is a gel-like substance that contains the cell’s DNA, ribosomes, and other essential molecules.
Prokaryotic cells come in a variety of shapes, including spherical, rod-shaped, and spiral-shaped. The shape of a prokaryotic cell is often related to its function. For example, spherical cells are better at moving through liquids, while rod-shaped cells are better at attaching to surfaces.
2. Prokaryotic Cell Structure: Prokaryotic Cells Worksheet Answer Key
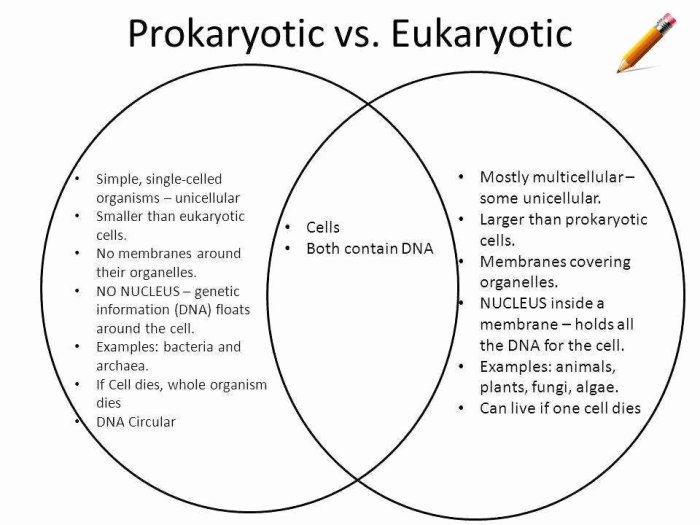
| Cell Structure | Description | Function | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell membrane | A thin, flexible layer that surrounds the cell | Protects the cell from its surroundings and regulates the passage of materials into and out of the cell | [Image of a cell membrane] |
| Cytoplasm | A gel-like substance that fills the cell | Contains the cell’s DNA, ribosomes, and other essential molecules | [Image of cytoplasm] |
| Ribosomes | Small, round structures that are found in the cytoplasm | Synthesize proteins | [Image of ribosomes] |
| Nucleoid | A region of the cytoplasm that contains the cell’s DNA | Stores the cell’s genetic information | [Image of a nucleoid] |
| Flagella | Long, whip-like structures that are used for locomotion | Help the cell to move through its environment | [Image of flagella] |
3. Prokaryotic Cell Function
Prokaryotic cells are capable of a wide variety of metabolic processes. They can use a variety of organic and inorganic compounds as sources of energy and carbon. Prokaryotic cells are also able to fix nitrogen, which is essential for the growth of plants.
Prokaryotes play an important role in nutrient cycling and environmental processes. They are responsible for the decomposition of organic matter, the cycling of nitrogen and sulfur, and the production of oxygen. Prokaryotes are also used in a variety of industrial processes, such as the production of antibiotics and biofuels.
Prokaryotic cells have evolved a variety of adaptations that allow them to survive in a wide range of environments. Some prokaryotes are able to live in extreme heat, cold, or acidity. Others are able to survive in the absence of oxygen.
4. Prokaryotic Cell Division
Prokaryotic cells reproduce by binary fission. Binary fission is a process in which a cell divides into two identical daughter cells. The process begins with the replication of the cell’s DNA. The two copies of the DNA are then separated and each copy is attached to a different pole of the cell.
The cell then elongates and a new cell membrane forms between the two copies of the DNA. The two daughter cells are then separated.
The FtsZ protein is essential for cell division in prokaryotes. FtsZ is a protein that forms a ring around the cell membrane. The FtsZ ring contracts and pulls the two daughter cells apart.
The rate of cell division in prokaryotes is regulated by a variety of factors, including the availability of nutrients and the temperature of the environment.
5. Prokaryotic Cell Diversity

Prokaryotes are a diverse group of organisms. They can be divided into two main groups: bacteria and archaea. Bacteria are the most common type of prokaryote. They are found in a wide variety of habitats, including soil, water, and the human body.
Archaea are less common than bacteria. They are found in extreme environments, such as hot springs and deep-sea hydrothermal vents.
Prokaryotes vary greatly in size, shape, and habitat. Some prokaryotes are as small as 0.1 micrometers in diameter, while others are as large as 100 micrometers in diameter. Prokaryotes can be spherical, rod-shaped, or spiral-shaped. They can be found in a wide variety of habitats, including soil, water, the human body, and extreme environments.
Prokaryotic cell diversity is important for the biosphere. Prokaryotes play a vital role in nutrient cycling, environmental processes, and the production of oxygen. They are also used in a variety of industrial processes.
6. Prokaryotic Cell Evolution

Prokaryotic cells are the oldest type of cells on Earth. They evolved from a common ancestor about 3.5 billion years ago. Prokaryotes were the only type of cell on Earth for about 2 billion years. During this time, they evolved a wide variety of adaptations that allowed them to survive in a wide range of environments.
The endosymbiotic theory is a theory that explains the origin of eukaryotic cells. The theory states that eukaryotic cells evolved from a symbiotic relationship between a prokaryotic cell and a bacterium. The bacterium was able to live inside the prokaryotic cell and provide it with energy.
In return, the prokaryotic cell provided the bacterium with a protected environment.
The endosymbiotic theory is supported by a number of lines of evidence, including the fact that eukaryotic cells contain organelles that are similar to bacteria. For example, mitochondria are similar to bacteria in terms of their size, shape, and DNA.
The endosymbiotic theory is one of the most important theories in biology.
FAQ Overview
What are the key characteristics of prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles, have a single circular chromosome, and possess ribosomes for protein synthesis.
How do prokaryotes divide?
Prokaryotes divide through binary fission, a process where the cell replicates its chromosome and divides into two identical daughter cells.
What is the significance of the FtsZ protein in cell division?
The FtsZ protein forms a ring-like structure that guides the formation of the septum, which divides the cell into two daughter cells.