Dna structure and replication packet – Delving into the intricacies of DNA structure and replication, this comprehensive guide unveils the fundamental principles governing the blueprint of life. Prepare to embark on an enlightening journey into the molecular realm, where genetic information unfolds its secrets.
DNA Structure: Dna Structure And Replication Packet
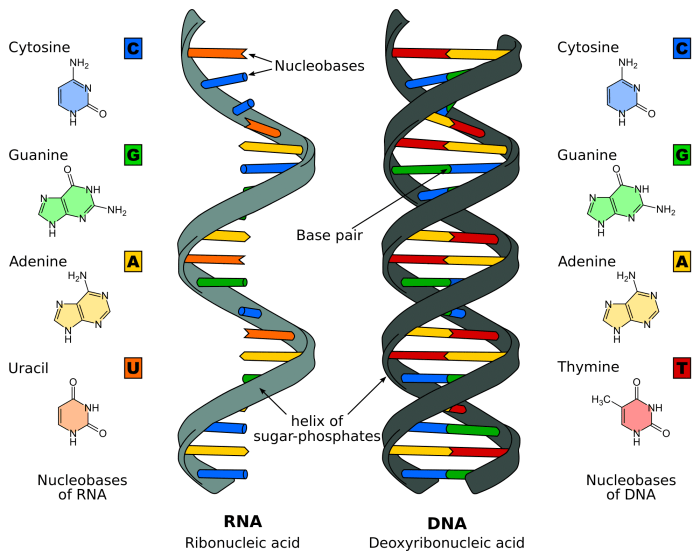
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that contains the genetic instructions for an organism. It is found in the nucleus of cells and is made up of two long chains of nucleotides twisted into a double helix.
Components of DNA, Dna structure and replication packet
Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. There are four different types of nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Adenine always pairs with thymine, and guanine always pairs with cytosine.
This is known as the base pairing rule.
DNA Replication
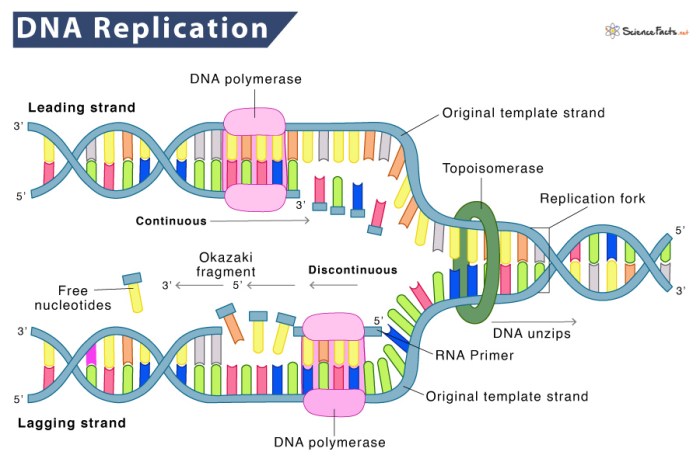
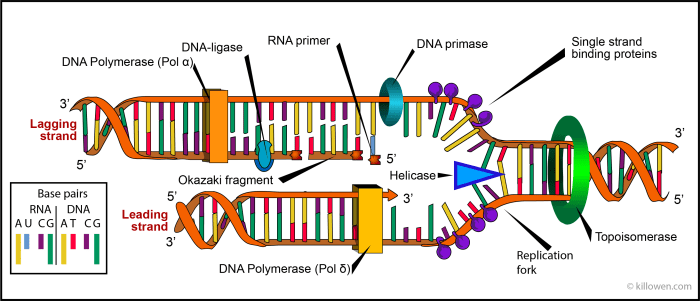
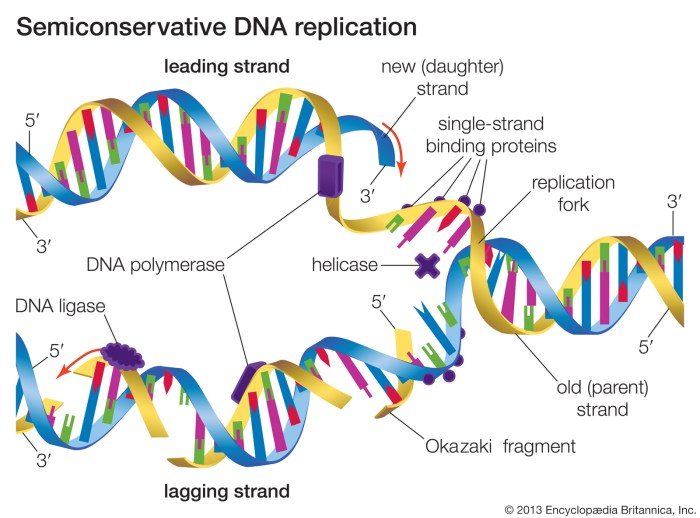
DNA replication is the process by which DNA makes a copy of itself. This process occurs before a cell divides, so that each new cell has its own copy of the DNA.
Steps of DNA Replication
- The DNA double helix unwinds and the two strands separate.
- Each strand of DNA acts as a template for the synthesis of a new strand.
- Enzymes called DNA polymerases add nucleotides to the new strands, following the base pairing rule.
- Once the new strands are complete, they wind around each other to form a new double helix.
DNA Replication Packet
The DNA replication packet should be organized into the following sections:
- Introduction
- DNA Structure
- DNA Replication
- Applications of DNA Structure and Replication
Each section should include a table summarizing the key concepts of that section.
The flowchart illustrating the process of DNA replication should include the following steps:
- The DNA double helix unwinds and the two strands separate.
- Each strand of DNA acts as a template for the synthesis of a new strand.
- Enzymes called DNA polymerases add nucleotides to the new strands, following the base pairing rule.
- Once the new strands are complete, they wind around each other to form a new double helix.
Applications of DNA Structure and Replication
DNA structure and replication have a wide range of applications in fields such as medicine, forensics, and biotechnology.
- In medicine, DNA structure and replication are used to diagnose and treat genetic diseases.
- In forensics, DNA structure and replication are used to identify criminals and victims.
- In biotechnology, DNA structure and replication are used to create genetically modified organisms.
FAQ Corner
What is the significance of the double helix structure of DNA?
The double helix structure, discovered by Watson and Crick, provides stability and protection for the genetic information stored within DNA.
How does DNA replication ensure accurate transmission of genetic information?
DNA replication involves proofreading mechanisms and DNA repair pathways that minimize errors, ensuring the faithful transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
What are the practical applications of DNA structure and replication?
Applications range from medical diagnostics and genetic engineering to forensic analysis and evolutionary studies, providing valuable insights into human health, agriculture, and the history of life.