Mole ratios pogil lab answer key – Unveiling the intricacies of mole ratios, this guide serves as a definitive resource for navigating the complexities of chemical reactions and stoichiometry. Delving into the concept of mole ratios, we embark on a journey that unravels their significance in balancing chemical equations, determining reactant and product quantities, and guiding laboratory experiments with precision.
Through a meticulous exploration of real-world applications and step-by-step problem-solving techniques, this guide empowers students and practitioners alike to master the art of mole ratios, ensuring a thorough understanding of their fundamental principles and practical implications.
Introduction to Mole Ratios
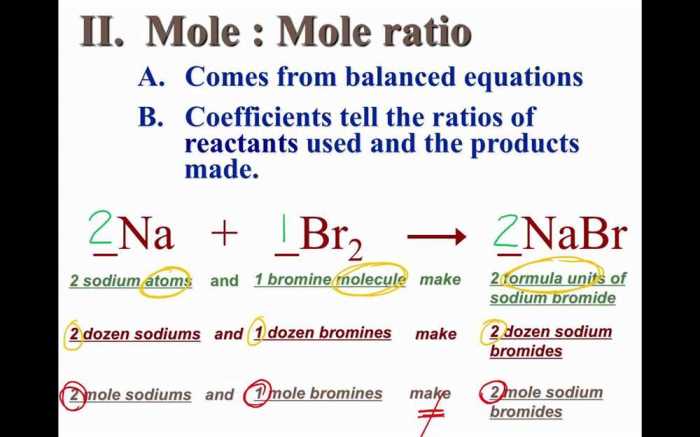
Mole ratios are mathematical expressions that describe the stoichiometric relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. They provide a way to determine the quantitative relationship between the moles of each substance involved in the reaction.
Mole ratios are significant because they allow chemists to predict the amount of reactants and products needed or produced in a reaction. This information is essential for designing and carrying out chemical experiments, as well as for understanding the behavior of chemical systems.
Examples of Mole Ratios in Real-World Scenarios
- In the production of ammonia, the Haber process uses a mole ratio of 3 moles of hydrogen to 1 mole of nitrogen to produce 2 moles of ammonia.
- In the combustion of propane, the mole ratio is 1 mole of propane to 5 moles of oxygen, producing 3 moles of carbon dioxide and 4 moles of water.
- In the neutralization of an acid with a base, the mole ratio is 1 mole of acid to 1 mole of base, producing 1 mole of salt and 1 mole of water.
Balancing Chemical Equations using Mole Ratios
Balancing chemical equations using mole ratios involves adjusting the coefficients in front of each reactant and product to ensure that the number of moles of each element is the same on both sides of the equation.
Guide to Balancing Chemical Equations using Mole Ratios
- Write the unbalanced chemical equation.
- Create a table with columns for reactants and products.
- Create a row for each element present in the equation.
- Calculate the mole ratio for each element by dividing the number of moles of the element in the reactants by the number of moles of the element in the products.
- Adjust the coefficients in front of each reactant and product to match the mole ratios.
- Check the equation to ensure that the number of moles of each element is the same on both sides.
Stoichiometry and Mole Ratios: Mole Ratios Pogil Lab Answer Key
Stoichiometry is the study of the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. Mole ratios are a key tool in stoichiometry, as they provide a way to determine the amount of reactants and products involved in a reaction.
Using Mole Ratios to Determine Reactant and Product Amounts
- Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
- Calculate the mole ratio for the desired reactant or product.
- Multiply the known amount of the other reactant or product by the mole ratio to determine the amount of the desired reactant or product.
Applications of Mole Ratios in the Lab
Mole ratios are used in a variety of laboratory experiments, including titrations and gravimetric analysis.
Titrations, Mole ratios pogil lab answer key
In titrations, mole ratios are used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution by reacting it with a solution of known concentration.
Gravimetric Analysis
In gravimetric analysis, mole ratios are used to determine the mass of a substance by measuring the mass of its precipitate.
Common Errors and Misconceptions
- Incorrectly balancing chemical equations:Mole ratios must be used to ensure that the number of moles of each element is the same on both sides of the equation.
- Misinterpreting mole ratios:Mole ratios represent the stoichiometric relationship between reactants and products, not the actual amounts of substances present in a reaction.
- Using incorrect units:Mole ratios must be expressed in moles, not grams or other units.
Tips to Avoid Errors
- Check the mole ratios carefully before using them in calculations.
- Pay attention to the units of the mole ratios and make sure they are consistent with the units of the other quantities in the calculation.
- Be aware of the common errors and misconceptions associated with mole ratios and take steps to avoid them.
FAQs
What is the significance of mole ratios in chemical reactions?
Mole ratios provide the stoichiometric proportions of reactants and products, ensuring balanced chemical equations and accurate predictions of reaction outcomes.
How can mole ratios be used to solve stoichiometry problems?
By utilizing mole ratios as conversion factors, stoichiometry problems can be solved to determine the quantities of reactants or products involved in a chemical reaction.
What are common applications of mole ratios in laboratory experiments?
Mole ratios guide the design and execution of experiments, such as titrations and gravimetric analysis, enabling precise determination of unknown concentrations and sample compositions.