A cyber analyst is drafting a memorandum – As a cyber analyst embarks on the task of drafting a memorandum, they assume the mantle of a meticulous scribe, meticulously documenting the intricacies of cybersecurity incidents and charting a course for effective response. This guide delves into the essential elements of memorandum composition, empowering analysts to convey their findings with clarity, precision, and actionable insights.
Throughout this comprehensive treatise, we will explore the structure and purpose of a memorandum, delve into the intricacies of cybersecurity incident analysis, and illuminate the significance of risk assessment and impact analysis. We will also shed light on the development of recommendations and action plans, emphasizing the importance of effective communication and reporting.
By adhering to the principles Artikeld herein, cyber analysts can craft memoranda that serve as invaluable tools for decision-making and incident response.
Memorandum Structure: A Cyber Analyst Is Drafting A Memorandum
A memorandum, also known as a memo, is a written communication used to convey information within an organization or between organizations. It is typically used for formal and professional communication and follows a specific structure.
Common Memorandum Sections
- Header:Includes the title, date, sender, recipient, and subject line.
- Introduction:Briefly introduces the purpose of the memo.
- Body:Contains the main content of the memo, organized into paragraphs.
- Conclusion:Summarizes the main points and may include recommendations or next steps.
- Signature:Includes the sender’s name and title.
Best Practices
- Use clear and concise language.
- Organize the memo logically, with headings and subheadings as needed.
- Proofread the memo carefully before sending it.
Cybersecurity Incident Analysis
Cybersecurity incident analysis is the process of investigating and understanding a cybersecurity incident to determine its cause, impact, and potential consequences.
Key Steps
- Identification:Detecting and recognizing that an incident has occurred.
- Containment:Limiting the spread and impact of the incident.
- Investigation:Gathering and analyzing evidence to determine the cause and extent of the incident.
- Mitigation:Implementing measures to minimize the damage and prevent future incidents.
- Recovery:Restoring affected systems and data to a normal state.
Techniques
- Log analysis
- Network traffic analysis
- System configuration analysis
- Malware analysis
Technical Details and Mitigation Strategies
Documenting the technical details of a cybersecurity incident is crucial for understanding the incident and developing effective mitigation strategies.
Guidance
- Collect logs, network traffic, and system configurations.
- Analyze the data to identify the source and impact of the incident.
- Develop mitigation strategies based on the analysis.
- Implement mitigation strategies to prevent or minimize future incidents.
Examples
- Implementing firewalls and intrusion detection systems to prevent unauthorized access.
- Using anti-malware software to detect and remove malicious software.
- Backing up data regularly to minimize the impact of a ransomware attack.
Risk Assessment and Impact Analysis

Risk assessment and impact analysis are critical for understanding the potential risks and consequences of a cybersecurity incident.
Methods
- Threat assessment:Identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities.
- Risk analysis:Evaluating the likelihood and impact of potential threats.
- Impact analysis:Assessing the financial, operational, and reputational impact of a cybersecurity incident.
Factors to Consider
- Type of incident
- Size and scope of the incident
- Sensitivity of data involved
- Potential impact on business operations
Recommendations and Action Plan
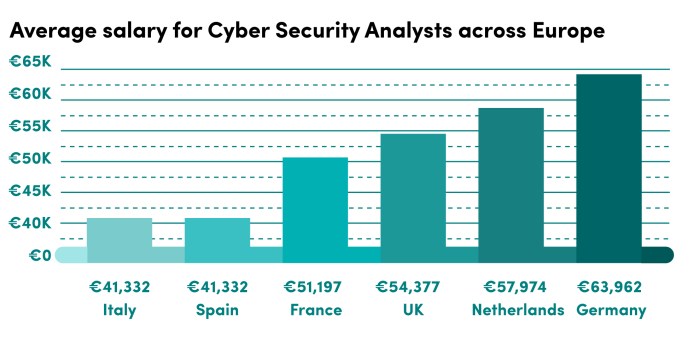
Based on the incident analysis, recommendations and an action plan should be developed to address identified risks and vulnerabilities.
Process, A cyber analyst is drafting a memorandum
- Identify risks and vulnerabilities.
- Develop recommendations to mitigate risks.
- Create an action plan to implement recommendations.
Examples
- Recommendation:Implement a multi-factor authentication system to enhance security.
- Action Plan:Procure and deploy multi-factor authentication devices, train users on their use, and monitor the system for effectiveness.
Communication and Reporting
Effective communication is essential in incident response to ensure that all stakeholders are informed and can take appropriate action.
Importance
- Keep stakeholders informed about the incident.
- Coordinate response efforts.
- Maintain transparency and credibility.
Guidance
- Communicate clearly and concisely.
- Use multiple communication channels (e.g., email, phone, instant messaging).
- Document all communication.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Cybersecurity incident response must comply with applicable legal and regulatory requirements.
Requirements
- Data protection and privacy laws
- Incident reporting requirements
- Cooperation with law enforcement
Role of Law Enforcement
- Investigate cybersecurity incidents.
- Enforce cybersecurity laws.
- Assist in incident response.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is essential for enhancing cybersecurity incident response capabilities.
Importance
- Identify areas for improvement.
- Update incident response plans.
- Enhance security posture.
Methods
- Review incident response plans regularly.
- Conduct exercises and simulations.
- Seek feedback from stakeholders.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the primary purpose of a memorandum in cybersecurity incident response?
A memorandum serves as a formal record of an incident, providing a comprehensive overview of its technical details, impact analysis, and recommendations for mitigation and future prevention.
What key elements should be included in a cybersecurity incident memorandum?
A well-crafted memorandum typically includes an executive summary, incident description, technical analysis, risk assessment, recommendations, and an action plan.
How can cyber analysts ensure the accuracy and credibility of their memoranda?
Analysts should rely on verifiable evidence, conduct thorough investigations, and consult with subject matter experts to ensure the accuracy and credibility of their findings and recommendations.