Muscular strength is the quizlet, the ultimate guide to understanding the intricacies of muscular strength, its importance, and how to develop and maintain it. Delve into the fascinating world of muscular strength and discover its profound impact on your overall health and well-being.
This comprehensive guide explores the physiological basis of muscular strength, the different types of strength, and the factors that influence it. Learn about the various methods used to assess muscular strength and its significance for daily activities, athletic performance, and injury prevention.
Definition of Muscular Strength

Muscular strength refers to the ability of a muscle or group of muscles to exert force against resistance. It is a fundamental component of physical fitness and plays a crucial role in various daily activities, sports, and occupational tasks.
The physiological basis of muscular strength lies in the contractile properties of muscle fibers. When a muscle is stimulated by a nerve impulse, calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, triggering the interaction between actin and myosin filaments, resulting in muscle contraction.
Types of Muscular Strength
There are different types of muscular strength, each with its specific characteristics:
- Isometric Strength:The muscle generates force without changing its length. For example, holding a weight in a static position.
- Isotonic Strength:The muscle generates force while changing its length. For example, lifting a weight through a range of motion.
- Concentric Strength:The muscle generates force while shortening. For example, lifting a weight upwards.
- Eccentric Strength:The muscle generates force while lengthening. For example, lowering a weight slowly.
Factors Affecting Muscular Strength
Muscular strength is a complex trait influenced by various factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing strength training and achieving desired results.Genetics, training, nutrition, and recovery play significant roles in determining an individual’s muscular strength. Let’s delve into each factor and explore its impact:
Genetics
Genetic factors contribute to muscle fiber composition, size, and strength potential. Individuals with a higher proportion of fast-twitch muscle fibers, known for their power and strength, tend to have an advantage in strength-building activities.
Training
Regular strength training is the primary factor that enhances muscular strength. Progressive overload, involving gradually increasing the weight, sets, or repetitions, stimulates muscle growth and adaptation. Different training modalities, such as weightlifting, resistance band exercises, and plyometrics, can be employed to build strength effectively.
Nutrition
Proper nutrition is essential for muscle growth and recovery. Adequate protein intake is crucial for muscle protein synthesis, the process of building new muscle tissue. Additionally, carbohydrates provide energy for intense training sessions, while healthy fats support hormone production and recovery.
Recovery
Sufficient rest and recovery are vital for muscular strength development. During rest, muscles repair and rebuild, preparing them for subsequent training sessions. Sleep, hydration, and stress management contribute to optimal recovery and muscle growth.
Methods for Assessing Muscular Strength
Measuring muscular strength accurately is crucial for evaluating athletic performance, rehabilitation progress, and overall health. Various methods are employed to assess muscular strength, each with its advantages and limitations.
Dynamometry
Dynamometry involves using specialized devices called dynamometers to measure the force generated by a muscle or muscle group. Handheld dynamometers are commonly used for grip strength assessment, while isokinetic dynamometers measure strength at different joint angles and speeds.
Advantages:Objective and quantifiable measurements, allowing for precise comparisons over time. Limitations:May not accurately reflect functional strength in real-world scenarios, and expensive equipment is required.
Manual Muscle Testing
Manual muscle testing (MMT) is a clinical assessment method where a healthcare professional manually applies resistance against a muscle and assigns a numerical grade based on the muscle’s ability to overcome resistance.
Advantages:Widely accessible, cost-effective, and provides a qualitative assessment of muscle strength. Limitations:Subjective and prone to inter-rater variability, making comparisons challenging.
Other Methods
- Jump tests:Measure explosive power and lower-body strength by assessing vertical jump height.
- Pull-ups and push-ups:Bodyweight exercises that provide an indirect measure of upper-body strength.
- Timed tests:Evaluate functional strength by measuring the time taken to perform tasks like chair stands or stair climbing.
Choosing the appropriate method depends on the specific assessment goals, available resources, and the individual’s condition.
Importance of Muscular Strength
Muscular strength is of paramount importance for overall health and fitness. It plays a vital role in performing daily activities, enhancing athletic performance, and preventing injuries.
Strong muscles support the body’s skeletal framework, enabling us to move, lift, and carry objects with ease. They facilitate balance, coordination, and agility, allowing for efficient and graceful movement.
Role in Daily Activities, Muscular strength is the quizlet
Muscular strength is essential for everyday tasks such as climbing stairs, carrying groceries, and lifting heavy objects. It enables us to maintain good posture, reduce fatigue, and perform physically demanding jobs.
Role in Athletic Performance
For athletes, muscular strength is crucial for power, speed, and endurance. It improves running, jumping, throwing, and lifting abilities. Strong muscles enhance athletic performance by generating greater force and allowing for more efficient movements.
Role in Injury Prevention
Strong muscles provide stability and support to joints, ligaments, and tendons. They help absorb impact, reduce stress on the musculoskeletal system, and prevent injuries during falls or accidents.
Developing Muscular Strength
Developing muscular strength is crucial for improving overall fitness, enhancing athletic performance, and maintaining a healthy body composition. Here’s a step-by-step guide to effectively develop muscular strength:
It’s important to note that developing muscular strength requires consistency, patience, and proper form. Consult with a qualified fitness professional before beginning any new exercise program, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
Progressive Overload
To develop muscular strength, you need to gradually increase the amount of resistance you lift over time. This principle is known as progressive overload. As your muscles adapt to the current level of resistance, they become stronger, necessitating an increase in resistance to continue stimulating muscle growth.
- Start with a weight or resistance level that challenges you while maintaining good form.
- Gradually increase the weight or resistance by small increments (5-10%) once you can comfortably perform 8-12 repetitions of an exercise.
- Rest adequately between sets and exercises to allow for muscle recovery and repair.
Compound Exercises
Compound exercises are multi-joint movements that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously. These exercises are highly effective for building overall strength and muscle mass.
- Squats: Target the quads, glutes, hamstrings, and core.
- Deadlifts: Work the back, hamstrings, glutes, and core.
- Bench press: Strengthens the chest, triceps, and shoulders.
- Pull-ups: Engage the back, biceps, and forearms.
Training Frequency and Volume
The frequency and volume of your strength training workouts will depend on your individual goals and fitness level. However, it’s generally recommended to train each muscle group 2-3 times per week.
- Beginners: Start with 2-3 sets of 8-12 repetitions per exercise.
- Intermediate: Aim for 3-4 sets of 8-12 repetitions per exercise.
- Advanced: Consider increasing sets to 4-5 and repetitions to 6-10.
Rest and Recovery
Rest and recovery are essential for muscle growth and strength development. Ensure adequate sleep (7-9 hours per night) and allow for rest days between workouts.
- Rest 1-2 minutes between sets.
- Take rest days when needed to prevent overtraining and promote recovery.
- Listen to your body and adjust your training plan accordingly.
Nutrition
Proper nutrition is vital for supporting muscle growth and recovery. Ensure a balanced diet that provides adequate protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats.
- Consume 1.6-2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day.
- Include complex carbohydrates in your diet to provide energy for workouts.
- Consume healthy fats to support hormone production and cell function.
Maintaining Muscular Strength
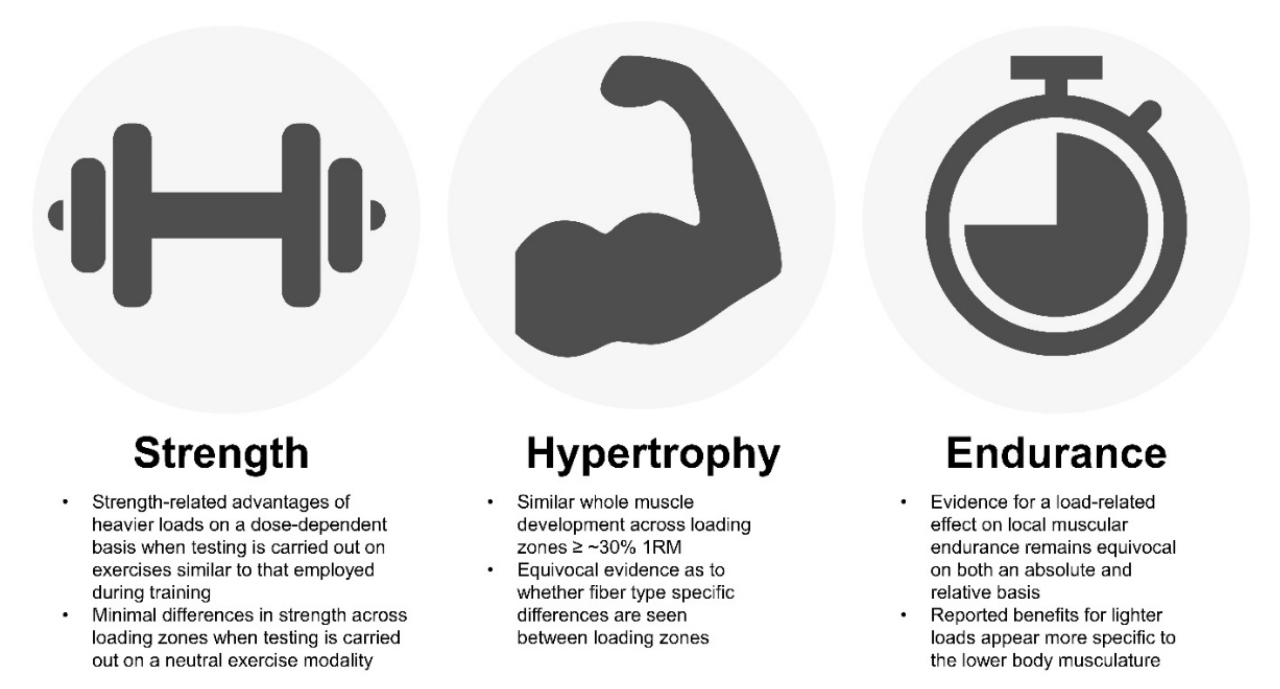
Maintaining muscular strength over time requires a comprehensive approach that includes regular training, proper nutrition, and adequate recovery.
Training Strategies
- Progressive Overload:Gradually increase the weight, resistance, or sets/reps over time to continuously challenge muscles and stimulate growth.
- Compound Exercises:Focus on exercises that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, maximizing efficiency and effectiveness.
- Variety and Periodization:Incorporate a variety of exercises and training methods to target different muscle fibers and prevent plateaus.
Nutritional Considerations
- Protein Intake:Consume sufficient protein to support muscle protein synthesis and repair, aiming for 1.6-2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight per day.
- Hydration:Stay well-hydrated as water is essential for muscle function and recovery.
- Nutrient-Rich Diet:Consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Recovery Techniques
- Rest and Sleep:Allow for adequate rest between workouts and ensure 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Active Recovery:Engage in light physical activity on rest days to promote blood flow and reduce muscle soreness.
- Stretching and Foam Rolling:Regularly stretch and use foam rolling to improve flexibility, reduce muscle tension, and aid in recovery.
Clarifying Questions: Muscular Strength Is The Quizlet
What is muscular strength?
Muscular strength is the ability of a muscle or group of muscles to exert force against resistance.
What are the different types of muscular strength?
The different types of muscular strength include isometric, isotonic, concentric, and eccentric.
How can I improve my muscular strength?
You can improve your muscular strength through regular resistance training, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises.
What are the benefits of having muscular strength?
Muscular strength is important for overall health and fitness, as it helps with daily activities, athletic performance, and injury prevention.