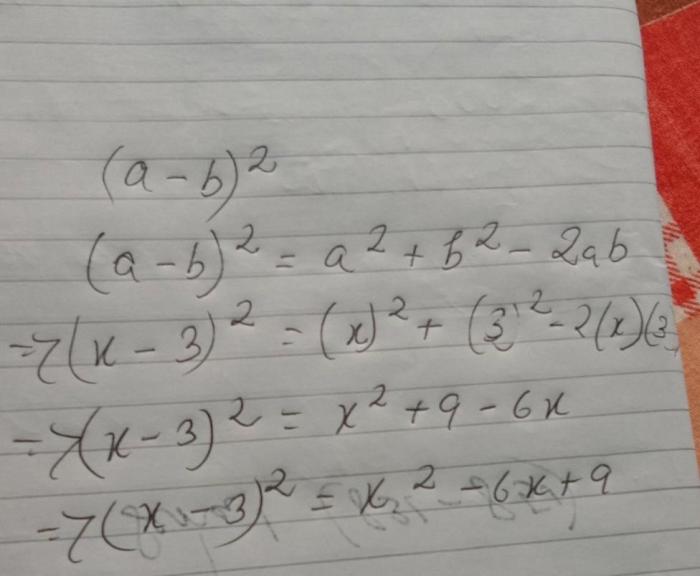Complete the square x2 6x 13 – Step into the world of algebra with “Complete the Square: An Effortless Guide to Mastering x^2 + 6x + 13.” Embark on an exciting journey where we unravel the mysteries of completing the square, a technique that transforms quadratic expressions into a simplified form, making them easier to solve.
Join us as we delve into the depths of mathematics, exploring its practical applications and unlocking its secrets.
Completing the square is not just a mathematical concept; it’s a gateway to problem-solving success. Whether you’re a student grappling with quadratic equations or an engineer tackling real-world challenges, this guide will empower you with the knowledge and skills to conquer any quadratic expression that comes your way.
Understanding the Concept: Complete The Square X2 6x 13

Completing the square is a technique used to rewrite a quadratic expression in the form (x + a)^2 + b. This form is useful for solving quadratic equations because it allows us to identify the vertex of the parabola represented by the equation, which is the point where the parabola changes direction.
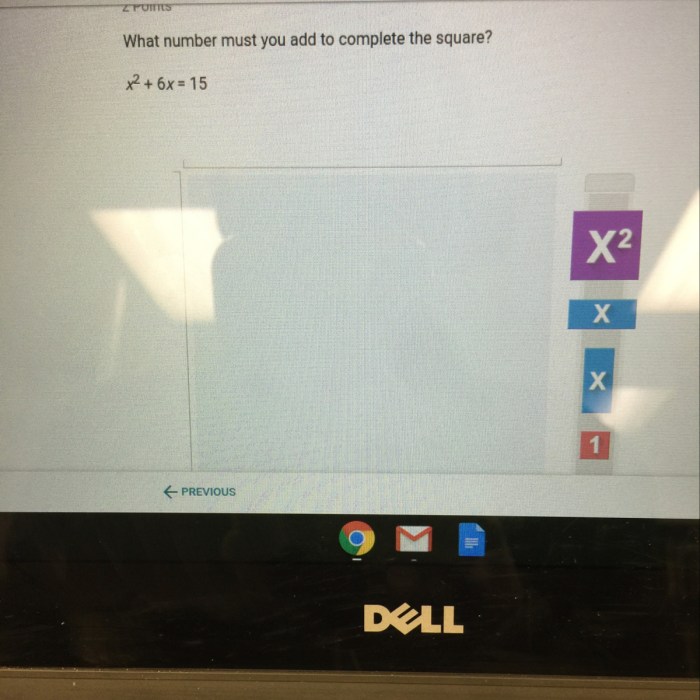
To complete the square for the expression x^2 + 6x + 13, we need to add and subtract the square of half the coefficient of x, which is (6/2)^2 = 9.
Steps to Complete the Square
- Add and subtract (6/2)^2 = 9 to the expression: x^2 + 6x + 9
9 + 13
- Simplify the expression: (x + 3)^2 + 4
The expression (x + 3)^2 + 4 is now in the form (x + a)^2 + b, where a = 3 and b = 4. The vertex of the parabola represented by this equation is (-3, 4).
Step-by-Step Procedure
Completing the square is a mathematical technique used to simplify quadratic expressions and solve equations involving them. Let’s break down the steps involved in completing the square for the expression x2+ 6 x+ 13:
Step 1: Divide the Coefficient of x by 2
Begin by dividing the coefficient of x(which is 6) by 2. This gives us 3.
Step 2: Square the Result, Complete the square x2 6x 13
Next, square the result obtained in Step 1. So, 3 2= 9.
Step 3: Add and Subtract the Result
Add the result from Step 2 (9) to the original expression. Then, subtract the same value from the expression. This gives us:
x2+ 6 x+ 13 + 9
9
Simplifying further:
x2+ 6 x+ 9
9 + 13
Step 4: Factor the Perfect Square Trinomial
The expression x2+ 6 x+ 9 is a perfect square trinomial, which can be factored as ( x+ 3) 2. So, our expression becomes:
(x+ 3) 2
9 + 13
Step 5: Simplify
Finally, simplify the expression by combining the constant terms:
(x+ 3) 2+ 4
And that’s it! We have successfully completed the square for the expression x2+ 6 x+ 13.
Mathematical Calculations
Completing the square involves transforming the expression into a perfect square trinomial. This process entails adding and manipulating terms to create a binomial squared.
Calculating the Square of Half the Coefficient of x
The first step is to calculate half the coefficient of x. In this case, the coefficient of xis 6, so half of that is 3:
h = 3
We then square this value:
h2= 3 2= 9
Adding and Subtracting the Square
Next, we add and subtract the calculated square to the original expression. This means adding 9 to the expression and then subtracting 9 from the expression:
x2+ 6x + 13 + 9
9
Simplifying this gives us:
(x2+ 6x + 9) + (13
9)
The first term is now a perfect square trinomial, while the second term simplifies to 4.
Resulting Quadratic Form
Completing the square transforms the quadratic equation into a more manageable form, known as the vertex form. The resulting quadratic form is:
a( x– h) 2+ k
where a, h, and kare constants.
Facilitating Solution
This form simplifies the solution of the quadratic equation by revealing the vertex of the parabola represented by the equation. The vertex is the point ( h, k), and it is the minimum or maximum point of the parabola.
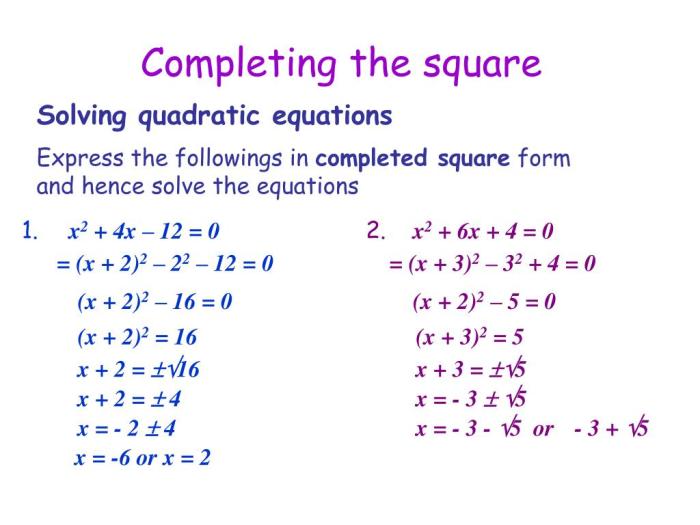
To complete the square of x2 + 6x + 13, we need to add and subtract the square of half the coefficient of x. Check out exercise 46 problems part 1 for more practice on completing the square. Returning to our problem, we have x2 + 6x + 13 = (x + 3)2 – 9 + 13 = (x + 3)2 + 4.
By identifying the vertex, we can quickly determine the:
- Axis of symmetry: x= h
- Direction of opening: Positive aindicates opening upward; negative aindicates opening downward
- x-intercepts: ( h± √(- k/ a), 0)
- y-intercept: (0, k)
This information provides a complete understanding of the parabola’s behavior and facilitates the graphical representation and analysis of the quadratic equation.
Examples and Applications
Let’s explore practical examples of completing the square and its applications in real-world scenarios.
Quadratic Expressions
Consider the quadratic expression x 2+ 6x + 13. To complete the square, we add and subtract (6/2) 2= 9 to the expression:
x2+ 6x + 9
9 + 13 = (x + 3)2+ 4
Solving Real-World Problems
Completing the square finds applications in various fields. For instance, in physics, it can be used to calculate the trajectory of a projectile:
h =
16t2+ vt + h 0
By completing the square, we can find the time it takes for the projectile to reach its maximum height:
t = v/32
Commonly Asked Questions
What is completing the square?
Completing the square is a mathematical technique used to transform a quadratic expression into a perfect square trinomial, making it easier to solve.
Why is completing the square useful?
Completing the square simplifies quadratic expressions, making it easier to find their roots and solve equations.
Can I use completing the square for any quadratic expression?
Yes, completing the square can be applied to any quadratic expression of the form ax^2 + bx + c.